goland 基础之map
map的内部结构
- go map是使用的哈希表构建的
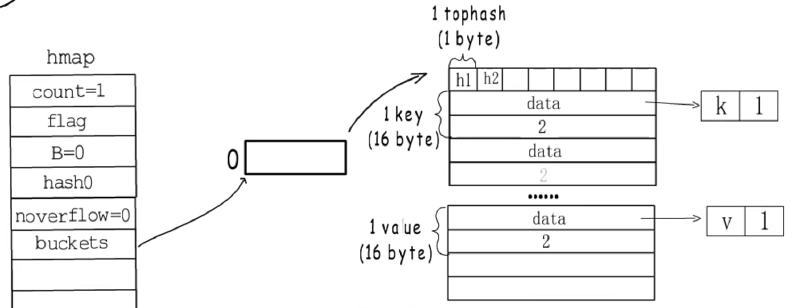
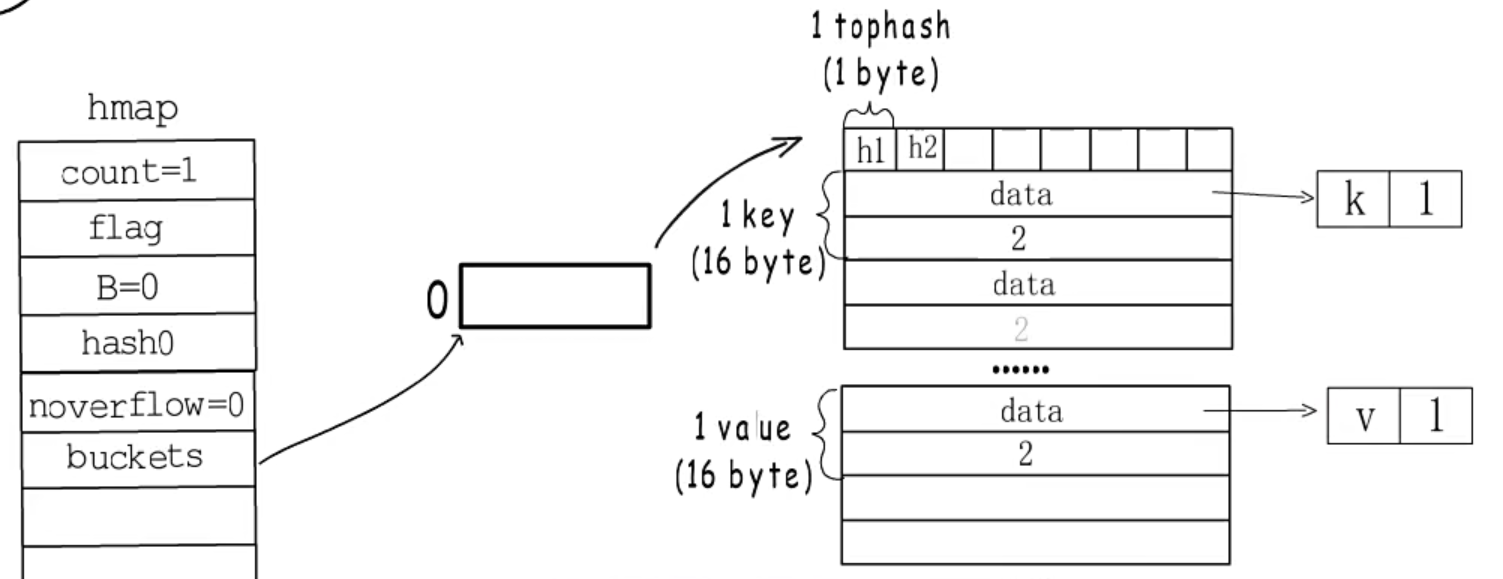
- map的结构可分为:hmap的结构体和bmap(桶),hmap结构体记录这map的基础信息(包括map存储个数, 桶的个数,hash种子,桶的数据,扩容时旧桶的数据以及迁移个数(map扩容不是一次性迁移完))
- 源码如下
定义hmap的结构:
type hmap struct {
// Note: the format of the hmap is also encoded in cmd/compile/internal/gc/reflect.go.
// Make sure this stays in sync with the compiler's definition.
// map 存储元素的计数
count int // # live cells == size of map. Must be first (used by len() builtin)
flags uint8 // map的状态标识,桶是否在增改,扩容或者缩容
//桶的个数/采用的与运算法计算桶的个数,桶的个数为2的整数次幂
B uint8 // log_2 of # of buckets (can hold up to loadFactor * 2^B items)
//溢出的桶的数量的近似值
noverflow uint16 // approximate number of overflow buckets; see incrnoverflow for details
hash0 uint32 // hash seed
//指向桶数据的指针
buckets unsafe.Pointer // array of 2^B Buckets. may be nil if count==0.
// 指向旧桶数据的指针
oldbuckets unsafe.Pointer // previous bucket array of half the size, non-nil only when growing
//扩容计数
nevacuate uintptr // progress counter for evacuation (buckets less than this have been evacuated)
// 保存溢出桶的链表和未使用的溢出桶数组的首地址
extra *mapextra // optional fields
}
// 桶的实现结构
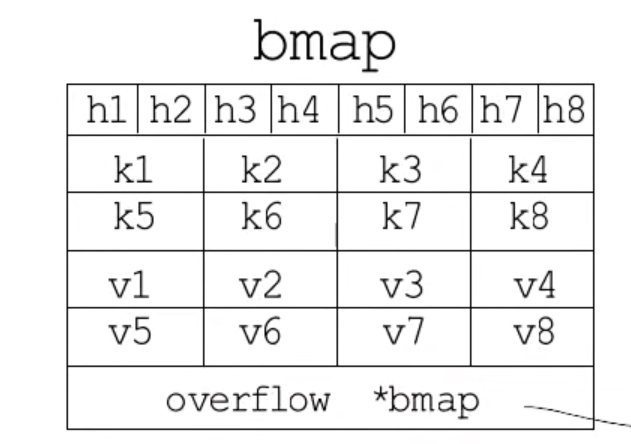
type bmap struct {
// 当前版本bucketCnt的值是8,一个桶最多存储8个key-value对
tophash [bucketCnt]uint8
}
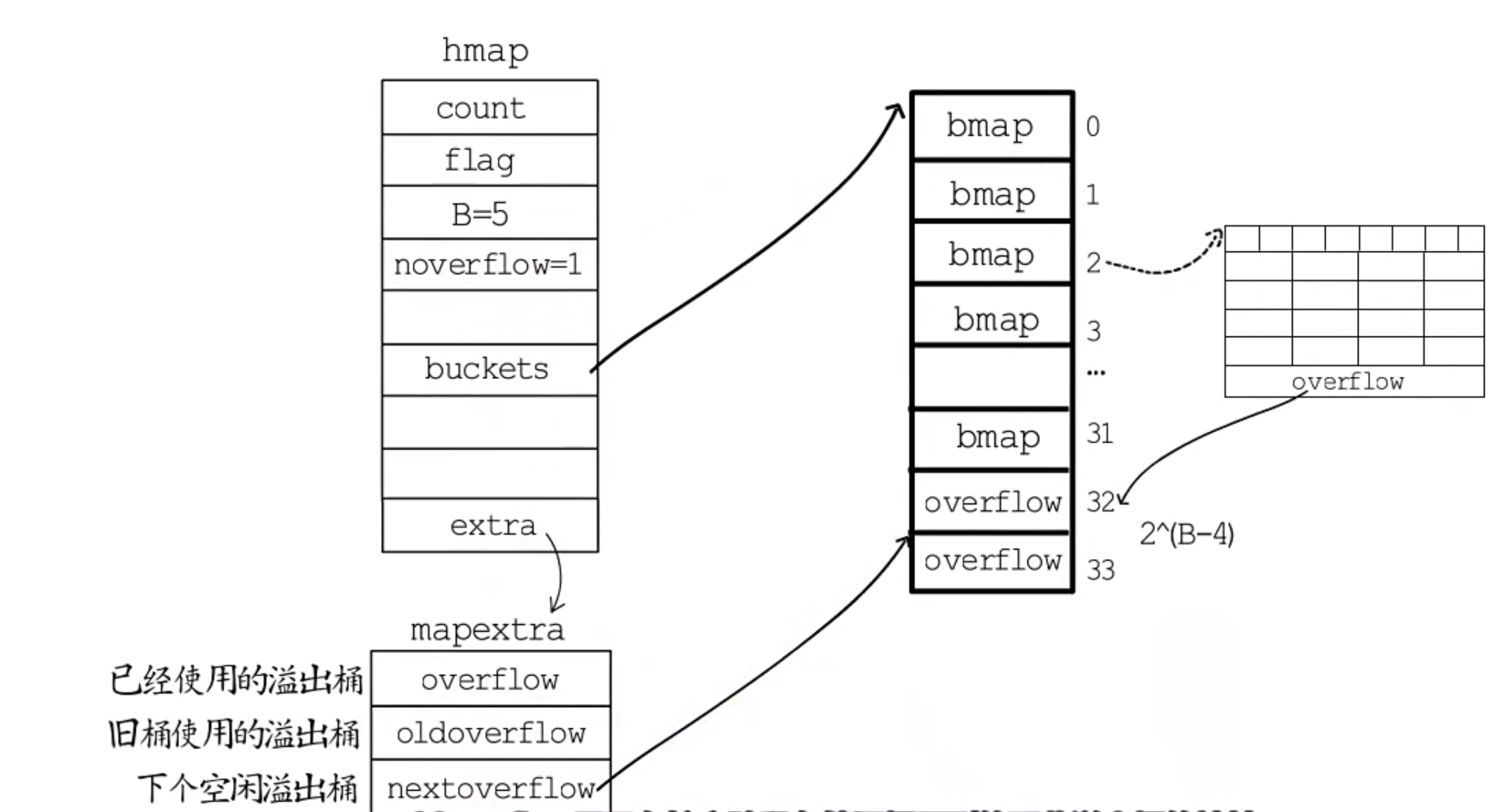
type mapextra struct {
// If both key and elem do not contain pointers and are inline, then we mark bucket
// type as containing no pointers. This avoids scanning such maps.
// However, bmap.overflow is a pointer. In order to keep overflow buckets
// alive, we store pointers to all overflow buckets in hmap.extra.overflow and hmap.extra.oldoverflow.
// overflow and oldoverflow are only used if key and elem do not contain pointers.
// overflow contains overflow buckets for hmap.buckets.
// oldoverflow contains overflow buckets for hmap.oldbuckets.
// The indirection allows to store a pointer to the slice in hiter.
overflow *[]*bmap //记录已经被使用的溢出桶
oldoverflow *[]*bmap // 扩容阶段旧的溢出桶
// nextOverflow holds a pointer to a free overflow bucket.
nextOverflow *bmap //指向下一个空闲的溢出桶
}
- 当桶的个数大于2的4次方时就会使用溢出桶源码如下
func makeBucketArray(t *maptype, b uint8, dirtyalloc unsafe.Pointer) (buckets unsafe.Pointer, nextOverflow *bmap) {
// 桶的个数
base := bucketShift(b)
nbuckets := base
// For small b, overflow buckets are unlikely.
// Avoid the overhead of the calculation.
if b >= 4 {
// 使用溢出桶
// Add on the estimated number of overflow buckets
// required to insert the median number of elements
// used with this value of b.
nbuckets += bucketShift(b - 4)//计算溢出桶的数量和不是溢出桶的数量的和
sz := t.bucket.size * nbuckets
up := roundupsize(sz)
if up != sz {
nbuckets = up / t.bucket.size //得出桶的数量
}
}
if dirtyalloc == nil {
// 没有被创建桶,申请创建桶的,返回桶的首地址
buckets = newarray(t.bucket, int(nbuckets))
} else {
// dirtyalloc was previously generated by
// the above newarray(t.bucket, int(nbuckets))
// but may not be empty.
buckets = dirtyalloc
size := t.bucket.size * nbuckets
if t.bucket.ptrdata != 0 {
memclrHasPointers(buckets, size)
} else {
memclrNoHeapPointers(buckets, size)
}
}
if base != nbuckets {
// We preallocated some overflow buckets.
// To keep the overhead of tracking these overflow buckets to a minimum,
// we use the convention that if a preallocated overflow bucket's overflow
// pointer is nil, then there are more available by bumping the pointer.
// We need a safe non-nil pointer for the last overflow bucket; just use buckets.
//空闲桶的地址
nextOverflow = (*bmap)(add(buckets, base*uintptr(t.bucketsize)))
last := (*bmap)(add(buckets, (nbuckets-1)*uintptr(t.bucketsize)))
last.setoverflow(t, (*bmap)(buckets))
}
return buckets, nextOverflow
}
func makemap(t *maptype, hint int, h *hmap) *hmap {
// 判断是否超过内存的限制
mem, overflow := math.MulUintptr(uintptr(hint), t.bucket.size)
if overflow || mem > maxAlloc {
hint = 0
}
// initialize Hmap
if h == nil {
h = new(hmap)
}
h.hash0 = fastrand()// 获取随机的hash值
// Find the size parameter B which will hold the requested # of elements.
// For hint < 0 overLoadFactor returns false since hint < bucketCnt.
B := uint8(0)
for overLoadFactor(hint, B) {
B++
}
h.B = B
// allocate initial hash table
// if B == 0, the buckets field is allocated lazily later (in mapassign)
// If hint is large zeroing this memory could take a while.
if h.B != 0 {
var nextOverflow *bmap
// 创建map的存储数据,返回的桶的数据的地址,下一个溢出桶的地址
h.buckets, nextOverflow = makeBucketArray(t, h.B, nil)
if nextOverflow != nil {
h.extra = new(mapextra)
h.extra.nextOverflow = nextOverflow
}
}
return h
}
-
当负载因子(loadFactorNum*(bucketShift(B)/loadFactorDen>6.5 -> 翻倍扩容
-
当负载因子小于6.5,但是溢出桶的数量大于2的15次方 -> 等量扩容
-
源代码如下:
// overLoadFactor reports whether count items placed in 1<<B buckets is over loadFactor.
// 负载因子大于6.5
func overLoadFactor(count int, B uint8) bool {
return count > bucketCnt && uintptr(count) > loadFactorNum*(bucketShift(B)/loadFactorDen)
}
// 溢出桶过多时
func tooManyOverflowBuckets(noverflow uint16, B uint8) bool {
// If the threshold is too low, we do extraneous work.
// If the threshold is too high, maps that grow and shrink can hold on to lots of unused memory.
// "too many" means (approximately) as many overflow buckets as regular buckets.
// See incrnoverflow for more details.
if B > 15 {
B = 15
}
// The compiler doesn't see here that B < 16; mask B to generate shorter shift code.
return noverflow >= uint16(1)<<(B&15)
}
// 扩容源码
func hashGrow(t *maptype, h *hmap) {
// If we've hit the load factor, get bigger.
// Otherwise, there are too many overflow buckets,
// so keep the same number of buckets and "grow" laterally.
bigger := uint8(1)
if !overLoadFactor(h.count+1, h.B) {
//等量扩容
bigger = 0
h.flags |= sameSizeGrow
}
oldbuckets := h.buckets
newbuckets, nextOverflow := makeBucketArray(t, h.B+bigger, nil)// 从新分配数据地址
flags := h.flags &^ (iterator | oldIterator)
if h.flags&iterator != 0 {
// 迭代的时候搬迁旧桶
flags |= oldIterator
}
// commit the grow (atomic wrt gc)
h.B += bigger // 桶的个数
h.flags = flags
h.oldbuckets = oldbuckets
h.buckets = newbuckets
h.nevacuate = 0
h.noverflow = 0
// 溢出桶钻便为旧溢出桶
if h.extra != nil && h.extra.overflow != nil {
// Promote current overflow buckets to the old generation.
if h.extra.oldoverflow != nil {
throw("oldoverflow is not nil")
}
h.extra.oldoverflow = h.extra.overflow
h.extra.overflow = nil
}
if nextOverflow != nil {
if h.extra == nil {
h.extra = new(mapextra)
}
h.extra.nextOverflow = nextOverflow
}
// the actual copying of the hash table data is done incrementally
// by growWork() and evacuate().
}