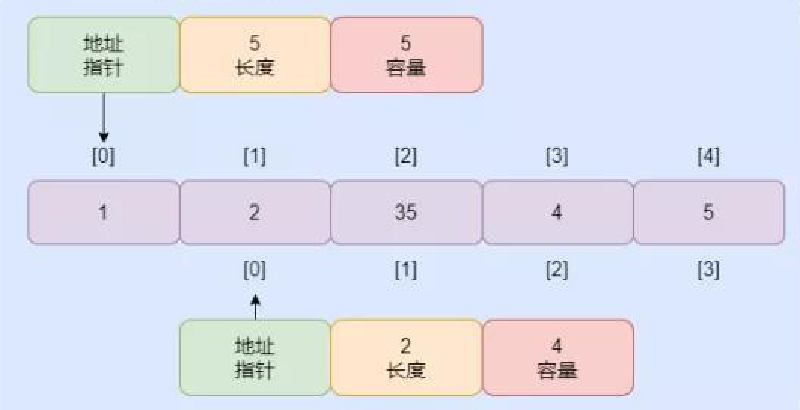
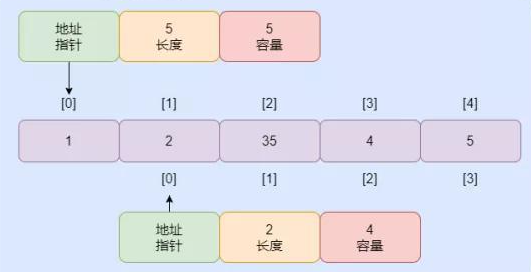
切片的内部结构
- 切片的结构可分为:数组,数据(元素)的地址&data、也存元素个数len、可以存储多少元素cap
- 源码如下
定义切片的结构:
type slice struct {
array unsafe.Pointer
len int
cap int
}
- 如图所示
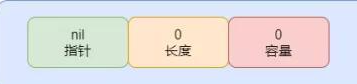
- var data [] int 声明一个切片,相当于生成切片的结构,data地址指针为nil, len和cap都为0。这就很清楚为什么,nil切片不可以直接使用了😄 结构如图
- 使用切片时需要make([]type,len,cap)或者初始化[]type{}才能使用,这是因为在在生成切片的结构时,同时也开辟了一段新的内存,类型为type, 结构长度为cap,同时值进行初始化。
- make 源码如下:
func makeslice(et *_type, len, cap int) unsafe.Pointer {
mem, overflow := math.MulUintptr(et.size, uintptr(cap)) // 判断是否越界
if overflow || mem > maxAlloc || len < 0 || len > cap {
// NOTE: Produce a 'len out of range' error instead of a
// 'cap out of range' error when someone does make([]T, bignumber).
// 'cap out of range' is true too, but since the cap is only being
// supplied implicitly, saying len is clearer.
// See golang.org/issue/4085.
mem, overflow := math.MulUintptr(et.size, uintptr(len))
if overflow || mem > maxAlloc || len < 0 {
panicmakeslicelen() // 越界直接 panic
}
panicmakeslicecap() // 越界直接 panic
}
return mallocgc(mem, et, true) //开辟内存
}
-
也可以通过底层数组初始化,切片的data指针指向就是相同类型的底层数组;通过slince := array[n:m],表示定义了一个类型和array相同,len为m-n,cap默认为array的长度的切片。切片和数组都指向了相同的地址。多个切片可以共用同一个底层数组。
avatar -
通过append 函数向切片增加切片的元素,增加了len, cap 不变。
切片扩容
-
在资源充裕的条件下,切片是可以通过append不断增加元素,当len个数增加到cap一样时,在增加元素时,就需要增加切片的容量cap,那问题来了,切片是怎么扩容的呢?
扩容规则(预估规则)
-
当需要扩容的数量比之前cap的两倍都大,则扩容为需要扩容的数量
-
当需要扩容的数量比之前cap的两倍都大小,之前的cap小于1024 直接扩大之前的2倍
-
当需要扩容的数量比之前cap的两倍都大小,之前的cap大于1024 直接扩大之前的1.25倍
-
伪代码如下
if oldcap2 < newcap 时, 扩容为newcap else{ if oldcap < 1024 newcap = 2oldcap ; else newcap = 1.25*oldcap }
-
源代码如下:
newcap := old.cap
doublecap := newcap + newcap //两倍的oldcap
if cap > doublecap {
//当需要扩容的数量比之前cap的两倍都大,则扩容为需要扩容的数量
newcap = cap
} else {
//当需要扩容的数量比之前cap的两倍都大小,之前的cap小于1024 直接扩大之前的2倍
if old.cap < 1024 {
newcap = doublecap
} else {
// Check 0 < newcap to detect overflow
// and prevent an infinite loop.
当需要扩容的数量比之前cap的两倍都大小,之前的cap大于1024 直接扩大之前的1.25倍
for 0 < newcap && newcap < cap {
newcap += newcap / 4
}
// Set newcap to the requested cap when
// the newcap calculation overflowed.
if newcap <= 0 {
newcap = cap
}
}
}
扩容调整
- 在预估扩容后,会根据内存对齐(减少内存浪费)在进行调整,代码:capmem := roundupsize(uintptr(newcap) * uintptr(et.size))newcap就是前文中计算出的newcap,et.size代表slice中一个元素的大小,capmem计算出来的就是此次扩容需要申请的内存大小。roundupsize函数就是处理内存对齐的函数
- 源码如下
var overflow bool
var lenmem, newlenmem, capmem uintptr
switch {
case et.size == 1: //例如byte 大小为1, 扩容的大小为向上取整的数值
lenmem = uintptr(old.len)
newlenmem = uintptr(cap)
capmem = roundupsize(uintptr(newcap))
overflow = uintptr(newcap) > maxAlloc
newcap = int(capmem)
case et.size == sys.PtrSize:
lenmem = uintptr(old.len) * sys.PtrSize
newlenmem = uintptr(cap) * sys.PtrSize
capmem = roundupsize(uintptr(newcap) * sys.PtrSize)
overflow = uintptr(newcap) > maxAlloc/sys.PtrSize
newcap = int(capmem / sys.PtrSize)
case isPowerOfTwo(et.size): //处理2的倍数
var shift uintptr
if sys.PtrSize == 8 {
// Mask shift for better code generation.
shift = uintptr(sys.Ctz64(uint64(et.size))) & 63
} else {
shift = uintptr(sys.Ctz32(uint32(et.size))) & 31
}
lenmem = uintptr(old.len) << shift
newlenmem = uintptr(cap) << shift
capmem = roundupsize(uintptr(newcap) << shift)
overflow = uintptr(newcap) > (maxAlloc >> shift)
newcap = int(capmem >> shift)
default:
lenmem = uintptr(old.len) * et.size
newlenmem = uintptr(cap) * et.size
capmem, overflow = math.MulUintptr(et.size, uintptr(newcap))
capmem = roundupsize(capmem)
newcap = int(capmem / et.size)
}
// The check of overflow in addition to capmem > maxAlloc is needed
// to prevent an overflow which can be used to trigger a segfault
// on 32bit architectures with this example program:
//
// type T [1<<27 + 1]int64
//
// var d T
// var s []T
//
// func main() {
// s = append(s, d, d, d, d)
// print(len(s), "\n")
// }
if overflow || capmem > maxAlloc {
panic(errorString("growslice: cap out of range"))
}
### 扩容后内存分配
* 分配 大于cap的内存,没有数据指针,memclrNoHeapPointers创建
* 源码如下:
>
var p unsafe.Pointer
if et.ptrdata == 0 {
p = mallocgc(capmem, nil, false)
// The append() that calls growslice is going to overwrite from old.len to cap (which will be the new length).
// Only clear the part that will not be overwritten.
memclrNoHeapPointers(add(p, newlenmem), capmem-newlenmem)
} else {
// Note: can't use rawmem (which avoids zeroing of memory), because then GC can scan uninitialized memory.
p = mallocgc(capmem, et, true) //分配内存地址
if lenmem > 0 && writeBarrier.enabled {
// Only shade the pointers in old.array since we know the destination slice p
// only contains nil pointers because it has been cleared during alloc.
bulkBarrierPreWriteSrcOnly(uintptr(p), uintptr(old.array), lenmem-et.size+et.ptrdata)
}
}
memmove(p, old.array, lenmem) //数据迁移
return slice{p, old.len, newcap}
}